Blog
What Is Shareholder Equity SE and How Is It Calculated?
- May 8, 2024
- Posted by: admin
- Category: Bookkeeping
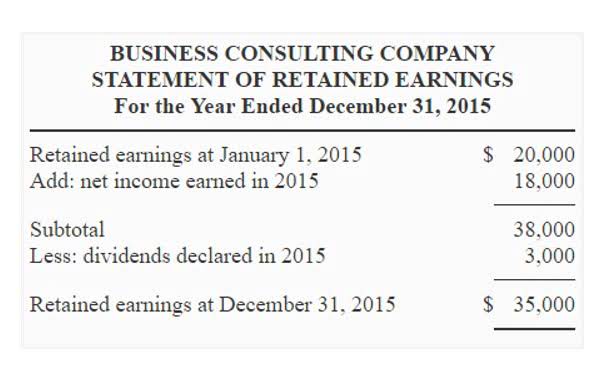
Aside from stock (common, preferred, and Treasury) components, the SE statement includes retained earnings, unrealized gains and losses, and contributed (additional paid-up) capital. Gains and losses that arise due to revaluation during the period must be presented in the statement of stockholder’s equity to the extent that they are recognized outside the statement of Accounting for Technology Companies comprehensive income. Analyzing the statement provides insight into the sources of equity capital and impacts on shareholder value.
Statement of Financial Position Balance Sheet
The statement of shareholders’ equity complements the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, forming the backbone of financial reporting. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity, with shareholders’ equity representing the residual interest in assets after liabilities. Treasury stock refers to shares repurchased from the open market and held by the company. These shares are not considered outstanding and do not carry voting rights or dividends. Share buybacks reduce the number of shares available, potentially increasing the value of remaining shares and improving financial ratios like earnings per share (EPS). Under GAAP, treasury stock is recorded as a contra-equity account, reducing total shareholders’ equity.
- Any other gains and losses not recognized in the income statement may be presented in the statement of changes in equity such as actuarial gains and losses arising from the application of IAS 19 Employee Benefit.
- Drawdowns might indicate the issuance of dividends or buy-back of shares, while a surge could be due to the company’s accumulation of profits.
- Careful preparation of this statement and review of equity changes will help assess financial strength and shareholder returns over time.
- Stockholders Equity provides highly useful information when analyzing financial statements.
- Current assets (cash, accounts receivable, inventory) are assets that can be converted to cash within a year.
Income Statement Profit & Loss Account
Firstly, it provides a comprehensive picture of a company’s financial condition. Looking at only one statement might give an incomplete image as changes in one can affect the other. For example, high profits (income statement) result in higher retained earnings, leading to an increase in shareholder’s equity (balance sheet). Now, the income statement provides details about a company’s revenue and expenses during a given period.

The Difference Between Big Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
As illustrated by this Home Depot statement, stockholders’ equity equals total paid-in capital plus retained earnings minus treasury stock. Common stockholders have more rights in the corporation in terms of voting on company decisions, but they are last on the priority list when it comes to paying. In the event of liquidation, common stockholders will be paid first, followed by bondholders and preference shareholders. The effect of correction of prior period errors must be presented separately in the statement of changes in equity as an adjustment to opening reserves. Note that the company had several equity transactions during the year, and the retained earnings column corresponds to a statement of retained earnings.

Statement of changes in equity helps users of financial statement to identify the factors that cause a change in the owners’ equity over the accounting periods. Stockholders’ equity represents the assets that belong to a company’s shareholders. It is calculated by subtracting total statement of stockholders equity liabilities from total assets and represents the residual interest or claim of shareholders to the assets of the company after deducting all liabilities. This financial statement summarizes on one page all of the changes that occurred in the stockholders’ equity accounts during the accounting year.
Revaluation gains and losses recognized during the period must be presented in the statement of changes in equity to the extent that they are recognized outside the income statement. This represents the profit or loss attributable to shareholders during the period as reported in the income statement. The statement of shareholders’ equity is also known as the statement of stockholders’ equity or the statement of equity.
Connection to the Income Statement
It can also tell whether you have enough equity in the company to weather a slump, such as the one caused by the COVID-19 epidemic. The Statement Of Shareholder Equity reveals whether you are in good enough shape to borrow from a bank, whether there is value in selling the business, and whether it makes sense for investors to contribute. A Statement Of Shareholder Equity helps you determine how adjusting entries successfully the business owner is conducting it.

Statement of Stockholders’ Equity
Financial health can be understood by analyzing the statement of equity as it gives a broad picture of the performance. Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment over periods longer than one year. Companies may have bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations under this category. If the company ever needs to be liquidated, SE is the amount of money that would be returned to these owners after all other debts are satisfied.
This is because it represents distribution of wealth that is attributable to stockholders. The resulting figure ($155,000) represents the shareholders’ equity or the ownership interest of stockholders in the corporation. Privately owned companies do not always have stockholders, so if your private business has never sold any equity shares, you don’t have to create a stockholders’ equity statement. However, if you are publicly owned (or if your private company has investors with equity in the business), you’ll want to understand what goes into creating this document so you can ensure you’re including the right information.
